Phone: (970) 439-4993
Our Services
Smiles Local Style is a Dental Hygenist office, in Steamboat Springs.
Dental deep cleaning, also known as scaling and root planing, is a procedure performed by a dental hygienist or dentist to treat advanced cases of periodontal disease. It is a more intensive cleaning procedure than a regular dental cleaning, and is usually performed over the course of two or more appointments.
During a deep cleaning, the dental professional will use specialized tools to remove plaque, tartar, and bacteria from the surfaces of the teeth and gums, including below the gumline. The hygienist or dentist will also smooth out any rough spots on the surfaces of the tooth roots, known as root planing, to help prevent bacteria from collecting there in the future.
Deep cleaning is typically recommended for patients with moderate to severe periodontal disease, as it can help to halt the progression of the disease and prevent further damage to the gums and bone that support the teeth. It may also be recommended for patients with other risk factors for gum disease, such as smokers or those with a family history of periodontal disease.
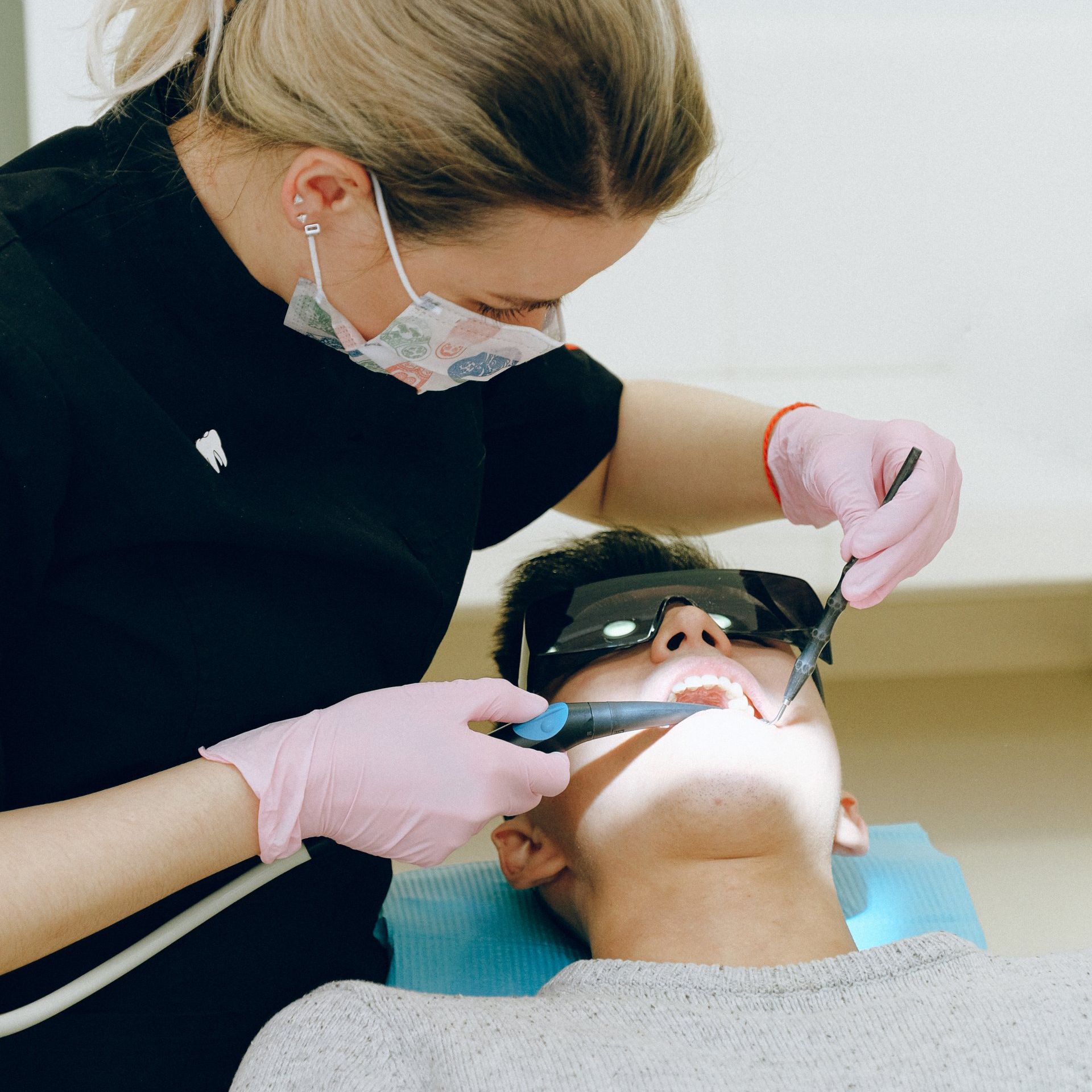
Some patients may experience some discomfort during or after a deep cleaning procedure, particularly if the gums are inflamed or sensitive. The dental professional may recommend over-the-counter pain relievers or prescribe medication to manage any discomfort.
After a deep cleaning, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene practices to prevent the buildup of bacteria and to promote healing. The dental professional may recommend special mouth rinses, changes to the patient's oral hygiene routine, or other steps to help promote healing and prevent further dental problems.
Overall, dental deep cleaning is an important tool for treating advanced cases of periodontal disease and preventing further damage to the teeth and gums. With proper care and maintenance, it can help patients to maintain good oral health and prevent more serious dental problems in the future.
About Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a bacterial infection that affects the tissues and structures that support and surround the teeth. It is a common and serious dental health issue that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
The earliest stage of periodontal disease is gingivitis, which is characterized by inflammation of the gums. Gingivitis is caused by a buildup of plaque on the teeth, which can irritate the gums and cause them to become red, swollen, and prone to bleeding.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which is a more severe form of gum disease. With periodontitis, the gums begin to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected with bacteria. The body's immune system responds by attacking the bacteria, but the resulting inflammation can damage the gums, bone, and connective tissue that support the teeth.
Over time, periodontitis can lead to the loss of teeth and other dental health problems. It has also been linked to an increased risk of certain systemic health conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory disease.
Treatment for periodontal disease depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases of gingivitis may be treated with improved oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, and a professional cleaning from a dental hygienist or dentist. More advanced cases of gum disease may require more extensive treatment, such as scaling and root planing (deep cleaning of the roots of the teeth), antibiotic therapy, or even surgery to remove damaged tissue.
Prevention is key to avoiding periodontal disease. Maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, can help remove plaque and prevent the buildup of bacteria. Regular dental checkups and cleanings can also help identify and treat gum disease in its early stages. Additionally, avoiding tobacco use, eating a balanced diet, and managing chronic health conditions can all help reduce the risk of developing periodontal disease.