Phone: (970) 439-4993
Our Services
Sue Calhoun is our Periodontal Disease specialist.
We are dental professionals who specialize in the treatment of periodontal disease. Known as periodontists, we received additional training and education beyond that of a general dentist or dental hygienist in the diagnosis and treatment of periodontal disease.
Periodontists are experts in the treatment of gum disease, and we often work closely with general dentists and other dental professionals to provide comprehensive care for our patients. We are trained to use a wide range of treatment methods to address periodontal disease, from non-surgical treatments like scaling and root planing to more advanced surgical procedures like gum grafting and bone regeneration.
In addition to treating periodontal disease, periodontists also specialize in the placement of dental implants. They can help patients who have lost teeth due to periodontal disease or other factors to restore their smiles and regain their oral health.
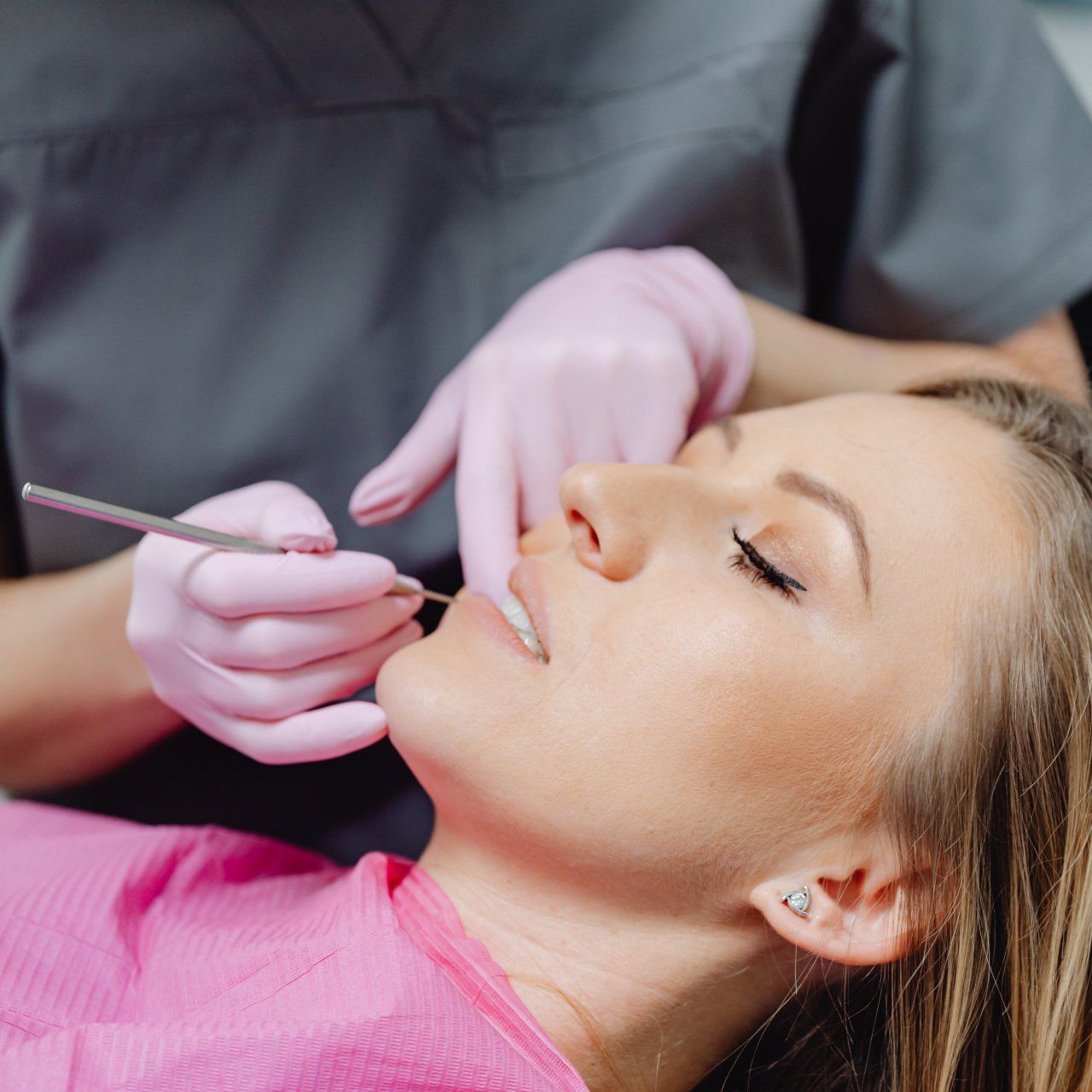
If you are experiencing symptoms of periodontal disease or have been diagnosed with gum disease, you may benefit from the care of a periodontist. Your general dentist can provide a referral to a periodontist in your area, or you can search for a qualified periodontist through professional organizations like the American Academy of Periodontology.
About Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a bacterial infection that affects the tissues and structures that support and surround the teeth. It is a common and serious dental health issue that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
The earliest stage of periodontal disease is gingivitis, which is characterized by inflammation of the gums. Gingivitis is caused by a buildup of plaque on the teeth, which can irritate the gums and cause them to become red, swollen, and prone to bleeding.
If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which is a more severe form of gum disease. With periodontitis, the gums begin to pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected with bacteria. The body's immune system responds by attacking the bacteria, but the resulting inflammation can damage the gums, bone, and connective tissue that support the teeth.
Over time, periodontitis can lead to the loss of teeth and other dental health problems. It has also been linked to an increased risk of certain systemic health conditions, such as heart disease, diabetes, and respiratory disease.
Treatment for periodontal disease depends on the severity of the condition. Mild cases of gingivitis may be treated with improved oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, and a professional cleaning from a dental hygienist or dentist. More advanced cases of gum disease may require more extensive treatment, such as scaling and root planing (deep cleaning of the roots of the teeth), antibiotic therapy, or even surgery to remove damaged tissue.
Prevention is key to avoiding periodontal disease. Maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing, can help remove plaque and prevent the buildup of bacteria. Regular dental checkups and cleanings can also help identify and treat gum disease in its early stages. Additionally, avoiding tobacco use, eating a balanced diet, and managing chronic health conditions can all help reduce the risk of developing periodontal disease.